Recombinant Human PD-L1-Fc Fusion Protein
| Product | Unit size | Cat. code | Docs. | Qty. | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
hPD-L1-Fc Soluble human PD-L1 fused to an IgG1 Fc domain |
Show product |
50 µg |
fc-hpdl1
|
|
Soluble human PD-L1 (CD274) fused to an IgG1 Fc domain

Potential applications of soluble hPD-L1-Fc protein
Protein description
 InvivoGen also offers:
InvivoGen also offers:
• Biosimilar IC antibodies
• Anti-IC cell-based assays (Bio-IC™)
• IC-expressing cell lines
InvivoGen offers hPD-L1-Fc, a soluble human PD-L1 (CD274) chimera protein generated by fusing the N-terminal extracellular domain of human PD-L1 (aa 19-238) to the N-terminus of a human IgG1 Fc domain with a TEV (Tobacco Etch Virus) sequence linker.
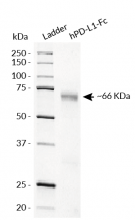
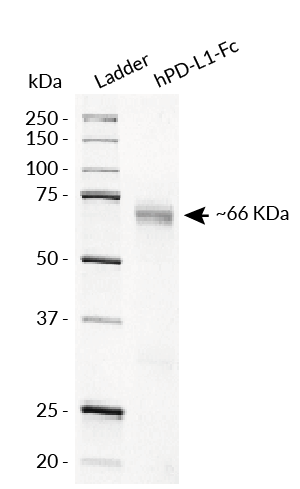
hPD-L1-Fc has been produced in CHO cells and purified by affinity chromatography. It has an apparent molecular weight of ~66 kDa on an SDS‑PAGE gel.
PD-L1 background
Programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1), also known as cluster of differentiation 274 (CD274) or B7 homolog 1 (B7-H1) is a Type I transmembrane protein that can be constitutively expressed or induced in myeloid, lymphoid, and normal epithelial cells, as well as in cancer [1, 2]. PD-L1 is classified as an inhibitory immune checkpoint. It is the principal ligand for programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) and under physiological conditions, this interaction is essential in the development of immune tolerance preventing excessive immune cell activity [1, 2].
Applications
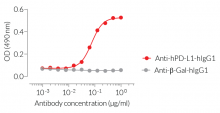
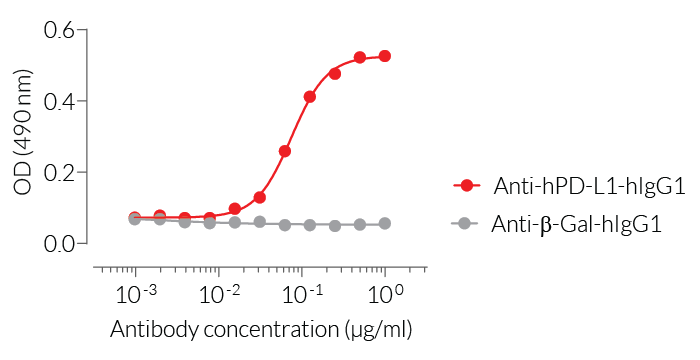
- Screening of high-affinity anti-human PD-L1 monoclonal antibodies by ELISA
- Screening of anti-human PD-1 monoclonal antibodies using competition assays
Quality control
- Size and purity confirmed by SDS-PAGE
- Protein validated by ELISA using an Anti-hPD-L1 mAb
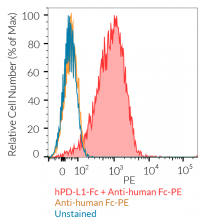
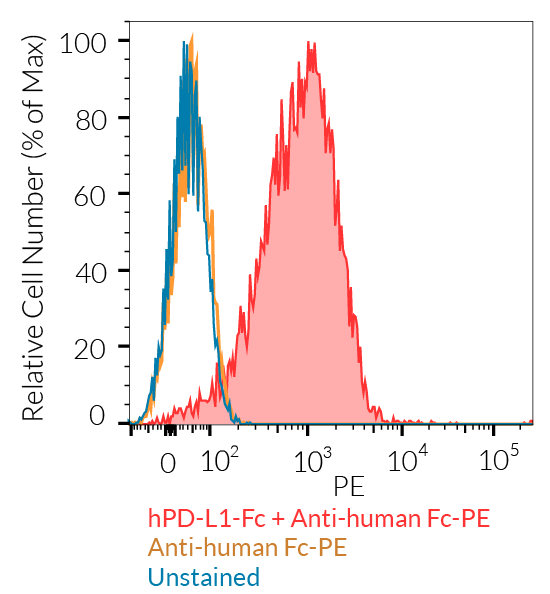
- Protein validated by FACS using Jurkat-Lucia™ TCR-hPD-1 cells
References
1. Juneja, V.R. et al. 2017. PD-L1 on tumor cells is sufficient for immune evasion in immunogenic tumors and inhibits CD8 T cell cytotoxicity. J Exp Med 214, 895-904.
2. Kythreotou, A. et al. 2018. PD-L1. J Clin Pathol 71, 189-194.
Specifications
Protein construction: N-terminal extracellular domain of human PD-L1 (aa 19-238) with a C-terminal human IgG1 Fc tag
Accession sequence: NP_054862.1
Species: Human
Source: CHO cells
Tag: C-terminal human IgG1 Fc
Total protein size: 463 a.a (secreted form)
Molecular weight: ~66 kDa (SDS-PAGE)
Purification: Protein G affinity chromatography
Purity: >98% (SDS-PAGE)
Quality control:
- The protein has been validated by ELISA upon incubation with Anti-hPD-L1-hIgG1.
- The protein has been validated by FACS using Jurkat-Lucia™ TCR-hPD-1 cells.
- The absence of bacterial contamination (e.g. lipoproteins and endotoxins) has been confirmed using HEK-Blue™ TLR2 and HEK-Blue™ TLR4 cellular assays.
Contents
- 50 µg lyophilized hPD-L1-Fc
- 1.5 ml endotoxin-free water
![]() The product is shipped at room temperature.
The product is shipped at room temperature.
![]() Store lyophilized product at -20°C.
Store lyophilized product at -20°C.
![]() Resuspended protein is stable for up to 1 month when stored at 4°C, and 1 year when stored at -20°C
Resuspended protein is stable for up to 1 month when stored at 4°C, and 1 year when stored at -20°C
Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
Back to the topDetails
Immune checkpoint signal: PD-1 and PD-L1
— PD-1 (programmed cell death 1; also known as CD279) is a type I transmembrane protein expressed at the cell surface of activated and exhausted conventional T cells. PD-1 is an inhibitory immune checkpoint that prevents T-cell overstimulation and host damage. PD-1 interaction with its ligands PD-L1 and PD-L2 induces inhibition of TCR signaling [1].
— PD-L1 (programmed cell death ligand 1; also known as CD274 or B7-H1) is a transmembrane protein expressed at the cell surface of hematopoietic and nonhematopoietic cells and is induced by pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as in the tumor microenvironment [1]. PD-L1 is one ligand for PD-1, an inhibitory immune checkpoint receptor that is expressed by activated and exhausted T cells. PD-1:PD-L1 interaction induces inhibition of TCR signaling, thereby preventing T-cell overstimulation and host damage [1].
PD-L1 expression is an immune evasion mechanism exploited by various malignancies and is generally associated with poorer prognosis [2]. Specifically, over-expressed PD-L1 on tumor cells and tumor-infiltrating immune cells, such as macrophages, can bind to PD-1 on cytotoxic T cells, and ultimately inhibit the anti-tumor T cell response [3, 4]. Thus, due to PD-L1’s instrumental role in immune evasion by cancer cells, there are numerous inhibitors in development as promising immuno-oncology therapies. Notably, Atezolizumab (also known as MPDL3280A), a fully humanized IgG1 (N298A) mAb that blocks the interaction of PD-L1 with PD-1 and induces anti-tumor immune reactivation, has been approved by the FDA for combinational use in the treatment of lung and breast cancer [3, 5].
References
1. Ribas A. and Wolchock J.D., 2018. Cancer immunotherapy using checkpoint blockade. Science. 359:1350-55.
2. Sun, C. et al. 2018. Regulation and Function of the PD-L1 Checkpoint. Immunity 48, 434-452.
3. Kythreotou, A. et al. 2018. PD-L1. J Clin Pathol 71, 189-194.
4. Lau, J. et al. 2017. Tumour and host cell PD-L1 is required to mediate suppression of anti-tumour immunity in mice. Nat Commun 8, 14572.
5. Heimes, A.S. & Schmidt, M. 2019. Atezolizumab for the treatment of triple-negative breast cancer. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 28, 1-5.