Anti-CD70 (Vorsetuzumab biosimilar) antibody family
| Product | Unit size | Cat. code | Docs. | Qty. | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Anti-hCD70-hIgG1 Human CD70 (Vorsetuzumab) antibody - Human IgG1 |
Show product |
100 µg 3 x 100 µg |
hcd70-mab1
|
|
||
|
Anti-hCD70-hIgG1fut Human CD70 (Vorsetuzumab) antibody - Human IgG1fut |
Show product |
100 µg 3 x 100 µg |
hcd70-mab13
|
|
||
|
Anti-hCD70-hIgG1NQ Human CD70 (Vorsetuzumab) antibody - Human IgG1NQ |
Show product |
100 µg 3 x 100 µg |
hcd70-mab12
|
|
Human monoclonal antibody (mAb) isotypes against human CD70

Anti-hCD70 mAb functions in cancer
(click to enlarge)
InvivoGen provides a family of anti-hCD70-derived monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) in multiple human isotypes. They feature
- the variable region of vorsetuzumab targeting the human (h)CD70 and
- a constant region that mediates different effector functions depending on the isotype.
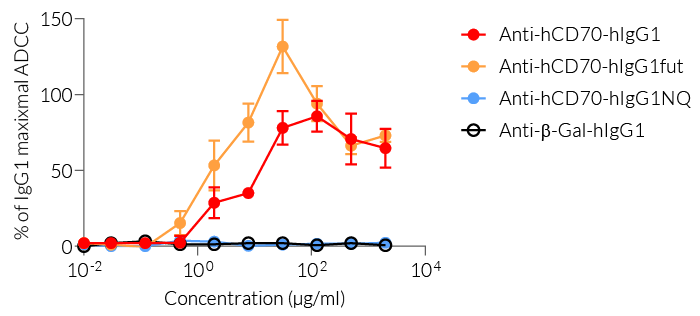
The effector functions of the human isotypes in this family include antibody‑dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) and complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC). You may choose between:
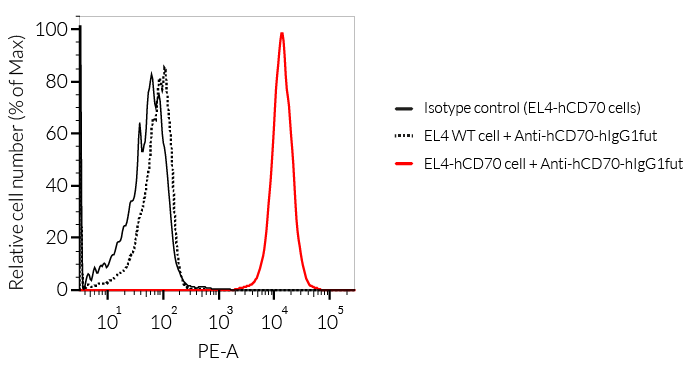
— IgG1 for high effector functions ('wild-type' hIgG1 constant region),
— IgG1fut for even higher effector functions (engineered non-fucosylated (fut) constant region), or
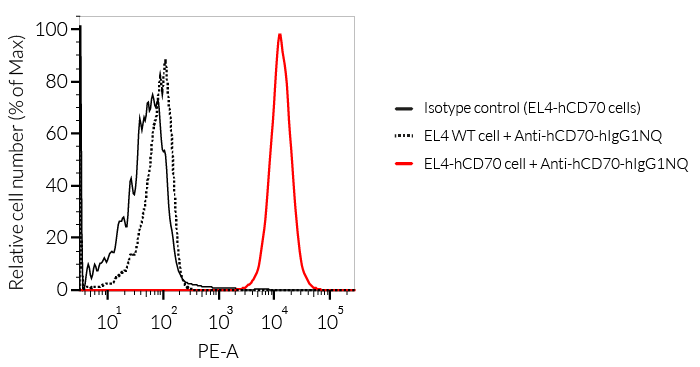
— IgG1NQ for no effector functions (engineered N-glycosylation mutated constant region).
InvivoGen's mAbs have been generated by recombinant DNA technology, produced in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells, and purified by affinity chromatography.
Anti-hCD70-hIgG1 is the biosimilar of the clinical antibody vorsetuzumab. Vorsetuzumab is a humanized IgG1 mAb targeting the immune checkpoint (IC) molecule CD70 (aka CD27 ligand or CD27L). This mAb can kill tumor cells through antibody-dependent cell-mediated responses (ADCC & ADCP). In addition, vorsetuzumab can also be conjugated with small molecular antitumor drugs to form a new type of targeted therapeutic molecule called antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) with accurate targeting and greater lethality [1]. Currently, a non-fucosylated version of this mAb (SEA-CD70) is undergoing clinical evaluation in a phase I study in patients with myeloid malignancies (NCT04227847) [2]. In the appropriate context of T cell receptor engagement, the interaction of CD27 with its ligand CD70 (also known as CD27L) promotes T cell activation, maturation of effector capacity, and T cell memory [3-4].
Key features of the Anti-hCD70 isotype family:
- Clinically-relevant variable region targeting human CD70 (vorsetuzumab)
- Choice of different constant regions for high/low effector functions
- Functionally validated by flow cytometry and ADCC assay
- The absence of bacterial contamination has been confirmed
InvivoGen’s products are for research use only, and not for clinical or veterinary use.
References:
1. Ryan MC, et al., 2010. Targeting pancreatic and ovarian carcinomas using the auristatin-based anti-CD70 antibody-drug conjugate SGN-75. Br J Cancer. 24;103(5):676-84.
2. Flieswasser, T., Van den Eynde, A., Van Audenaerde, J. et al., 2022. The CD70-CD27 axis in oncology: the new kids on the block. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 41, 12.
3. Vitale LA, et al.,2012. Development of a human monoclonal antibody for potential therapy of CD27-expressing lymphoma and leukemia. Clin Cancer Res.;18(14):3812-21.
4. Sanborn RE, et al., 2022. Safety, tolerability and efficacy of agonist anti-CD27 antibody (varlilumab) administered in combination with anti-PD-1 (nivolumab) in advanced solid tumors. J Immunother Cancer. 10(8):e005147.
Specifications
Specificity: Targets cells expressing human CD70
Clonality: Monoclonal antibodies
Clone: Vorsetuzumab (Anti-hCD70-hIgG1, kappa)
Isotype: Human IgG1
Control: Human IgG1, hIG1NQ, hIgG1fut
Source: Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells
Formulation: 0.2 μm filtered solution in a sodium phosphate buffer with glycine, saccharose, and stabilizing agents.
Tested Applications: Flow cytometry, ELISA, ADCC assay
Purification:
- hIgG1: purified by affinity chromatography with protein G
- hIgG1fut: purified by affinity chromatography with protein G
- hIgG1NQ: purified by affinity chromatography with protein G
Quality control:
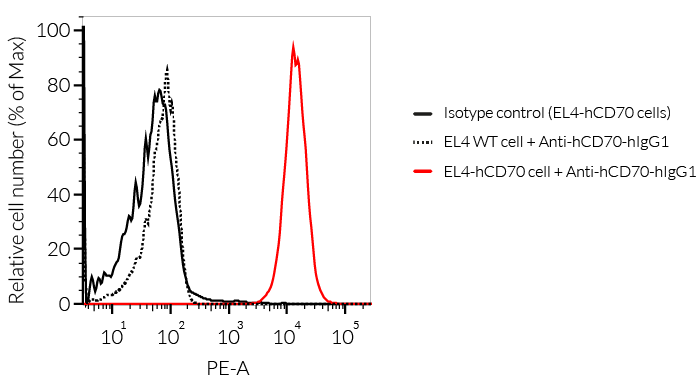
- The binding of Anti-hCD70 mAb to human CD70 on cells has been validated using flow cytometry.
- hIgG1 isotype effector function has been validated using an ADCC cellular assay.
- The complete sequence of the antibody has been verified.
- The absence of bacterial contamination (e.g. lipoproteins and endotoxins) has been confirmed using HEK-Blue™ hTLR2 and HEK-Blue™ TLR4 cellular assays.
Contents
Please note: Each product is sold separately. These purified monoclonal antibodies are provided azide-free and lyophilized.
Anti-hCD70-hIgG1 is available in two quantities:
- hcd70-mab1: 100 µg
- hcd70-mab1-03: 3 x 100 µg
Anti-hCD70-hIgG1fut is available in two quantities:
- hcd70-mab13: 100 µg
- hcd70-mab13-03: 3 x 100 µg
Anti-hCD70-hIgG1NQ is available in two quantities:
- hcd70-mab12: 100 µg
- hcd70-mab12-03: 3 x 100 µg
![]() Product is shipped at room temperature.
Product is shipped at room temperature.
![]() Upon receipt, store lyophilized antibody at -20 °C.
Upon receipt, store lyophilized antibody at -20 °C.
Tags: buy Vorsetuzumab (Anti-TNFSF7 / CD27L / CD70) | Vorsetuzumab (Anti-TNFSF7 / CD27L / CD70) supplier | purchase Vorsetuzumab (Anti-TNFSF7 / CD27L / CD70) | Vorsetuzumab (Anti-TNFSF7 / CD27L / CD70) cost | Vorsetuzumab (Anti-TNFSF7 / CD27L / CD70) manufacturer | order Vorsetuzumab (Anti-TNFSF7 / CD27L / CD70) | Vorsetuzumab (Anti-TNFSF7 / CD27L / CD70) distributor
Back to the topDetails
The Cluster of Differentiation CD70 (aka CD27L, TNFSF7), a member of the TNFR family, is known as the sole ligand for CD27. The CD27–CD70 costimulatory receptor-ligand pair plays an important role in immune regulation. In concert with the T cell receptor (TCR) crosslinking, it promotes T cell activation, proliferation, survival, maturation of effector capacity, and T cell memory [1-2]. CD70 is primarily expressed on antigen-presenting cells (APCs) and upon interaction,with T cell-expressed CD27, it initiates the necessary signaling required for the proliferation and differentiation of antigen-specific T cells. Interestingly, it has been established that CD70 itself is transiently expressed on T cells after their activation. Evidence shows that T cell-expressed CD70 plays an important immune checkpoint role in the suppression of inflammatory T cell responses by a number of mechanisms including the upregulation of inhibitory immune checkpoint molecules [3]. Thus, the expression of CD70 on T cells has the ability to ameliorate inflammation and therefore, may be beneficial in the treatment of inflammatory diseases, such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) [3].
Constitutive overexpression of CD70 has been described in a range of solid and hematological malignancies, whereby tumor cells have hijacked the CD27-CD70 signaling pathway to facilitate immune evasion in the tumor microenvironment (TME) [4]. They do this by increasing the amount of suppressive regulatory T cells (Tregs), inducing caspase-dependent apoptosis of T cells, and skewing T cells towards exhaustion, to ensure they circumvent the immune response [1]. Additionally, the presence of CD70 on cancer stem cells has been shown to be a predictive marker for metastasis and poor prognosis [5]. Exploiting CD70-targeting in cancer patients has the potential to specifically eliminate the CD70-expressing cancer cell populations and abrogate the tumor-promoting mechanisms by the CD70-CD27 signaling axis, both in the early stage and advanced disease. Combinatorial approaches with anti-CD70 targeting therapies have proven their potential in both preclinical and clinical settings, using antibody-mediated therapy, chemotherapy, and Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR)-T cell therapy [6].
In conclusion, CD70 targeting agents like CD70-directed mAbs bear the potential of effectively targeting CD70-expressing solid and hematological tumors. Further clinical trials are needed to investigate potential combinations of immune-modulating therapies, especially at earlier stages of disease, to achieve the best possible outcome for cancer patients [7].
References:
1. Jacobs, J. et al. 2015. CD70: An emerging target in cancer immunotherapy. Pharmacol Ther 155, 1-10.
2. Sanborn RE, et al., 2022 Safety, tolerability and efficacy of agonist anti-CD27 antibody (varlilumab) administered in combination with anti-PD-1 (nivolumab) in advanced solid tumors. J Immunother Cancer. 2022 Aug;10(8):e005147.
3. O'Neill, R.E. et al. 2017. T Cell-Derived CD70 Delivers an Immune Checkpoint Function in Inflammatory T Cell Responses. J Immunol 199, 3700-3710.
4. Jacobs, J. et al. 2018. Unveiling a CD70-positive subset of cancer-associated fibroblasts marked by pro-migratory activity and thriving regulatory T cell accumulation. Oncoimmunology 7, e1440167.
5. Liu, L. et al. 2018. Breast cancer stem cells characterized by CD70 expression preferentially metastasize to the lungs. Breast Cancer 25, 706-716.
6. Flieswasser, T., Van den Eynde, A., Van Audenaerde, J. et al. 2022. The CD70-CD27 axis in oncology: the new kids on the block. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 41, 12.
7. Starzer AM, Berghoff AS., 2020. New emerging targets in cancer immunotherapy: CD27 (TNFRSF7). ESMO Open. 4 (Suppl 3):e000629.
Back to the top